- Security >
- Encryption >
- In-Use Encryption >
- Introduction >
- Features
Features¶
On this page
Overview¶
On this page, you can learn about the security benefits of (), and how compares to other security mechanisms supported by MongoDB. You can also view a fictional scenario that demonstrates the value of
in securing your data.
() is a feature of MongoDB
that enables a client application to encrypt data before transporting it over the network. Sensitive data is transparently encrypted and decrypted by the client and only communicated to and from the server in encrypted form. keeps encrypted fields secure in the following scenarios:
- Direct access to encrypted fields by a database superuser
- Access to encrypted fields by reading the server’s memory
- Capture of encrypted fields over an insecure network
- Access to on-disk encrypted fields by reading database or backup files
While all clients have access to the non-sensitive data fields, only appropriately-configured clients are able to read and write the encrypted data fields.
Important
Remote
- When you use in production, you must use a remote
- (KMS) to store your encryption key.
To view a step-by-step guide demonstrating how to use a remote KMS with , see <csfle-tutorial-automatic-encryption>.
To view a list of all supported KMS providers, see <csfle-reference-kms-providers>.
To learn more about why you should use a remote KMS, see Reasons to Use a Remote KMS.
Other Security Mechanisms¶
This section describes the following security mechanisms supported by MongoDB and explains their use cases and limitations:
- <csfle-features-role-based-access-control>
- <csfle-features-encryption-at-rest>
- <csfle-features-transport-encryption>
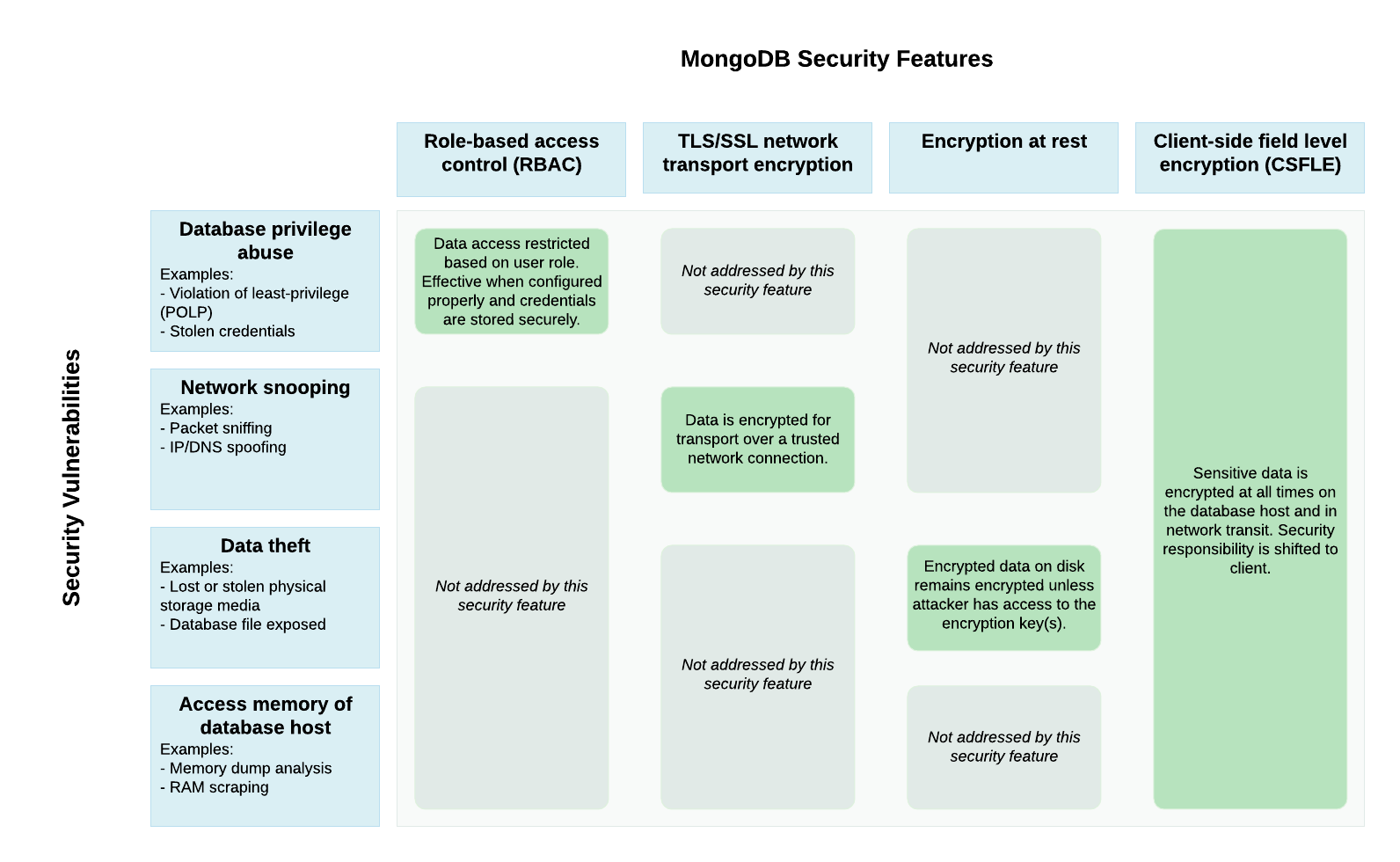
Role-Based Access Control¶
Role-Based Access Control is a security mechanism that allows administrators to grant and restrict collection-level permissions for users. With the appropriate role definition and assignment, this solution prevents accidental disclosure of data and access.
Role-Based Access control cannot protect against the following scenarios:
- Capture of the data over an insecure network
- Access to on-disk data by reading database or backup files
- Access to data by reading the server’s memory
- Direct access to data by a database superuser
To learn more, see Role-Based Access Control.
Encryption at Rest¶
Encryption at Rest is a mechanism that encrypts database files on disk. This mechanism prevents a person who lacks database credentials, but has access to the computer hosting your database, from viewing your data.
This mechanism does not protect your data against the following scenarios:
- Capture of the data over an insecure network
- Access to data by reading the server’s memory
- Direct access to data by a database superuser
To learn more, see Encryption at Rest.
Transport Encryption (TLS/SSL)¶
Transport Encryption using TLS/SSL encrypts your data over the network. TLS/SSL protects your data as it travels over an insecure network, but cannot protect your data from a privileged user or as it sits on disk.
To learn more, see Transport Encryption using TLS/SSL
Comparison of Features¶
The following diagram lists security features MongoDB supports and the potential security vulnerabilities that they address:
Important
Use the Mechanisms Together
To secure a production deployment, use all the security mechanisms discussed in this guide together. The mechanisms are not mutually exclusive.
Scenario¶
The following fictional scenario demonstrates the value of () in securing your application’s data, and how
interacts with the other security mechanism discussed
in this guide.
In this scenario, we secure sensitive data on a medical care management system that stores patients’ personal information, insurance information, and medical records for a fictional company, MedcoMD. None of the patient data is public, and specific data such as their social security number (SSN, a US government-issued id number), insurance policy number, and vital sign measurements are particularly sensitive and subject to privacy compliance. It is important for the company and the patient that the data is kept private and secure.
MedcoMD needs this system to satisfy the following use cases:
- Doctors use the system to access patients’ medical records, insurance information, and add new vital sign measurements.
- Receptionists use the system to verify patients’ identities using their contact information.
- Receptionists can view a patient’s insurance policy provider, but not their policy number.
- Receptionists cannot access a patient’s medical records.
MedcoMD is also concerned with the disclosure of sensitive data through any of the following methods:
- Accidental disclosure of data on a receptionist’s publicly-viewable screen.
- Direct access to the database by a superuser such as a database administrator.
- Capture of data over an insecure network.
- Access to data by reading the database server’s memory.
- Access to data by reading database or backup files.
What can MedcoMD do to balance the functionality and access restrictions of their medical care management system?
Solution¶
MedcoMD uses the following security mechanisms to satisfy their use cases and protect against the disclosure of sensitive medical data:
Transport Encryption (TLS/SSL) to secure data as it travels over the network.
Encryption at Rest to protect against disclosure of data by reading database or backup files.
Role-Based Access Control to limit the access of database users to the collections necessary for them to perform their tasks.
Encrypting sensitive fields with to satisfy the following use cases and constraints:
- Prevent reading data from server memory as the
encrypted data is never on the database server in
an unencrypted form.
Allow receptionists to verify patients’ identities and prevent accidental disclosure of sensitive data on a receptionist’s publicly viewable screen by providing receptionists with a client that is not -enabled.
Allow doctors to view sensitive data privately in their offices by providing doctors with a -enabled client.
Learn More¶
To view a list of security measures you should implement to protect your MongoDB deployment, see the Security Checklist.
To start using CSFLE, see the <csfle-quick-start>.