- Security >
- Encryption >
- In-Use Encryption >
- Introduction >
- Reference >
- KMS Providers
KMS Providers¶
On this page
Overview¶
Learn about the **** providers () supports.
A **** is a provided as a service.
Tasks
In , your performs the following tasks:
To learn more about s and s, see Keys and Key Vaults.
Create and Store your¶
To create a , you must configure your provider to generate your as follows:
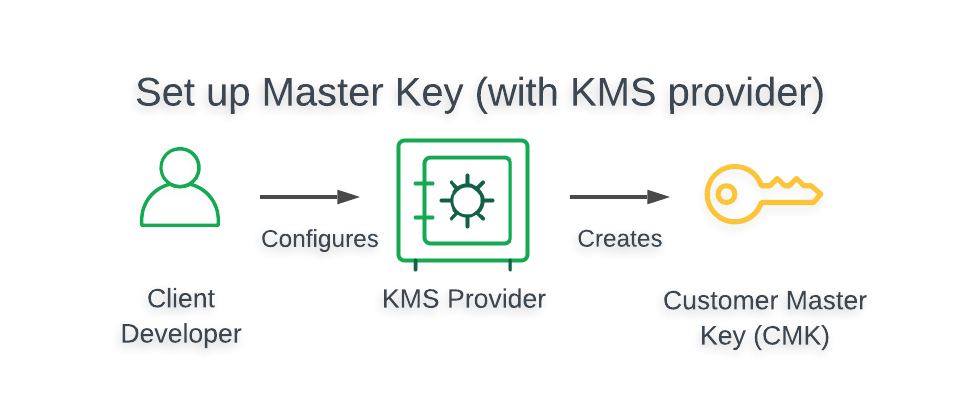
- To view a tutorial demonstrating how to create and store your
- in your preferred ,
see Tutorials.
Create and Encrypt a¶
When you create a , you must perform the following actions:
- Instantiate a
ClientEncryptioninstance in your -enabled application:- Provide a
kmsProvidersobject that specifies the credentials your -enabled application uses to authenticate with your .
- Provide a
- Create a with the
CreateDataKeymethod of theClientEncryptionobject in your -enabled application.- Provide a
dataKeyOptsobject that specifies with which key your should encrypt your new .
- Provide a
To view a tutorial demonstrating how to create and encrypt a , see the following resources:
To view the structure of kmsProviders and dataKeyOpts objects
for all supported providers, see
Supported Key Management Services.
Decrypt a¶
To decrypt a , you must provide a kmsProviders object
that specifies the credentials your -enabled
application uses to authenticate with your and retrieve
your .
To learn more about decrypting your , see How CSFLE Decrypts Documents.
Supported Key Management Services¶
The following sections of this page present the following information for all providers:
- Architecture of -enabled client
- Structure of
kmsProvidersobjects - Structure of
dataKeyOptsobjects
supports the following
providers:
Amazon Web Services KMS¶
This section provides information related to using AWS Key Management Service in your -enabled application.
To view a tutorial demonstrating how to use AWS KMS in your -enabled application, see Use Automatic with AWS.
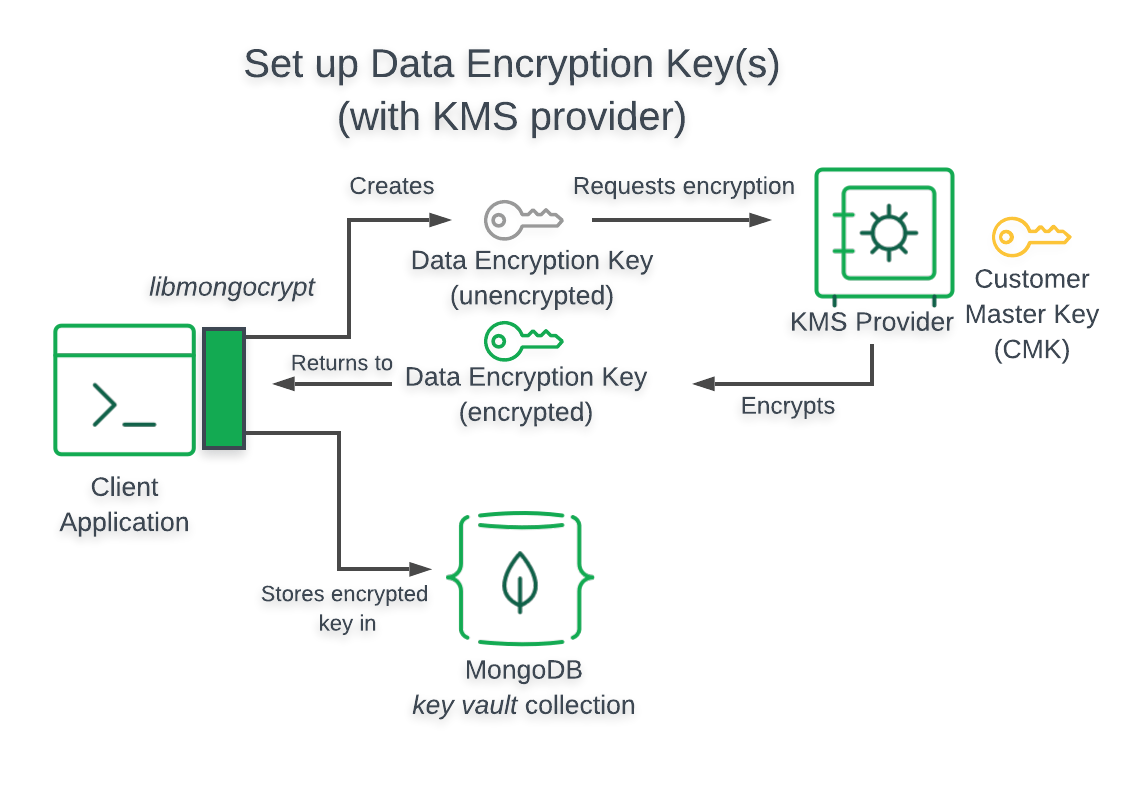
Architecture¶
The following diagram describes the architecture of a -enabled application using KMS.
Note
Client Can’t Access
When using the preceding , your -enabled application does not have access to your .
kmsProviders Object¶
The following table presents the structure of a kmsProviders
object for AWS KMS:
| Field | Required for IAM User | Required for IAM Role | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Access Key ID | Yes | Yes | Identifies the account user. |
| Secret Access Key | Yes | Yes | Contains the authentication credentials of the account user. |
| Session Token | No | Yes | Contains a token obtained from AWS Security Token Service (STS). |
dataKeyOpts Object¶
The following table presents the structure of a dataKeyOpts
object for AWS KMS:
| Field | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| key | Yes | Amazon Resource Number (ARN) of the master key. |
| region | No | AWS region of your master key, e.g. “us-west-2”; required only if not specified in your ARN. |
| endpoint | No | Custom hostname for the AWS endpoint if configured for your account. |
Azure Key Vault¶
This section provides information related to using Azure Key Vault in your -enabled application.
To view a tutorial demonstrating how to use Azure Key Vault in your -enabled application, see Use Automatic with Azure.
Architecture¶
The following diagram describes the architecture of a -enabled application using Azure Key Vault.

Note
Client Can’t Access
When using the preceding , your -enabled application does not have access to your .
kmsProviders Object¶
The following table presents the structure of a kmsProviders
object for Azure Key Vault:
| Field | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| azure.tenantId | Yes | Identifies the organization of the account. |
| azure.clientId | Yes | Identifies the clientId to authenticate your registered application. |
| azure.clientSecret | Yes | Used to authenticate your registered application. |
| azure.identityPlatformEndpoint | No | Specifies a hostname and port number for the authentication server. Defaults to login.microsoftonline.com and is only needed for non-commercial Azure instances such as a government or China account. |
dataKeyOpts Object¶
The following table presents the structure of a dataKeyOpts object for
Azure Key Vault:
| Field | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| keyName | Yes | Name of the master key |
| keyVersion | No | Version of the master key |
| keyVaultEndpoint | Yes | URL of the key vault. E.g. myVaultName.vault.azure.net |
Google Cloud Platform KMS¶
This section provides information related to using Google Cloud Key Management in your -enabled application.
To view a tutorial demonstrating how to use GCP KMS in your -enabled application, see Use Automatic with GCP.
Architecture¶
The following diagram describes the architecture of a -enabled application using GCP KMS.

Note
Client Can’t Access
When using the preceding , your -enabled application does not have access to your .
kmsProviders Object¶
The following table presents the structure of a kmsProviders
object for GCP KMS:
| Field | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Yes | Identifies your service account email address. | |
| privateKey | Yes | Identifies your service account private key in either
base64 string or
Binary subtype 0
format without the prefix and suffix markers.
Suppose your service account private key value is as follows:
The value you would specify for this field is:
If you have a
user-key.json credential file, you can extract
the string by executing the following command in a bash or
similar shell: |
| endpoint | No | Specifies a hostname and port number for the authentication server. Defaults to oauth2.googleapis.com. |
dataKeyOpts Object¶
The following table presents the structure of a dataKeyOpts object for
GCP KMS:
| Field | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| projectId | Yes | Identifier for your project in which you created the key. |
| location | Yes | Region specified for your key. |
| keyRing | Yes | Identifier for the group of keys your key belongs to. |
| keyName | Yes | Identifier for the symmetric master key. |
| keyVersion | No | Specifies the version of the named key. If not specified, the default version of the key is used. |
| endpoint | No | Specifies the host and optional port of the Cloud KMS. The default
is cloudkms.googleapis.com. |
KMIP¶
This section provides information related to using a KMIP compliant provider in your -enabled application.
To view a tutorial demonstrating how to use a KMIP compliant provider in your -enabled application, see Use Automatic with KMIP.
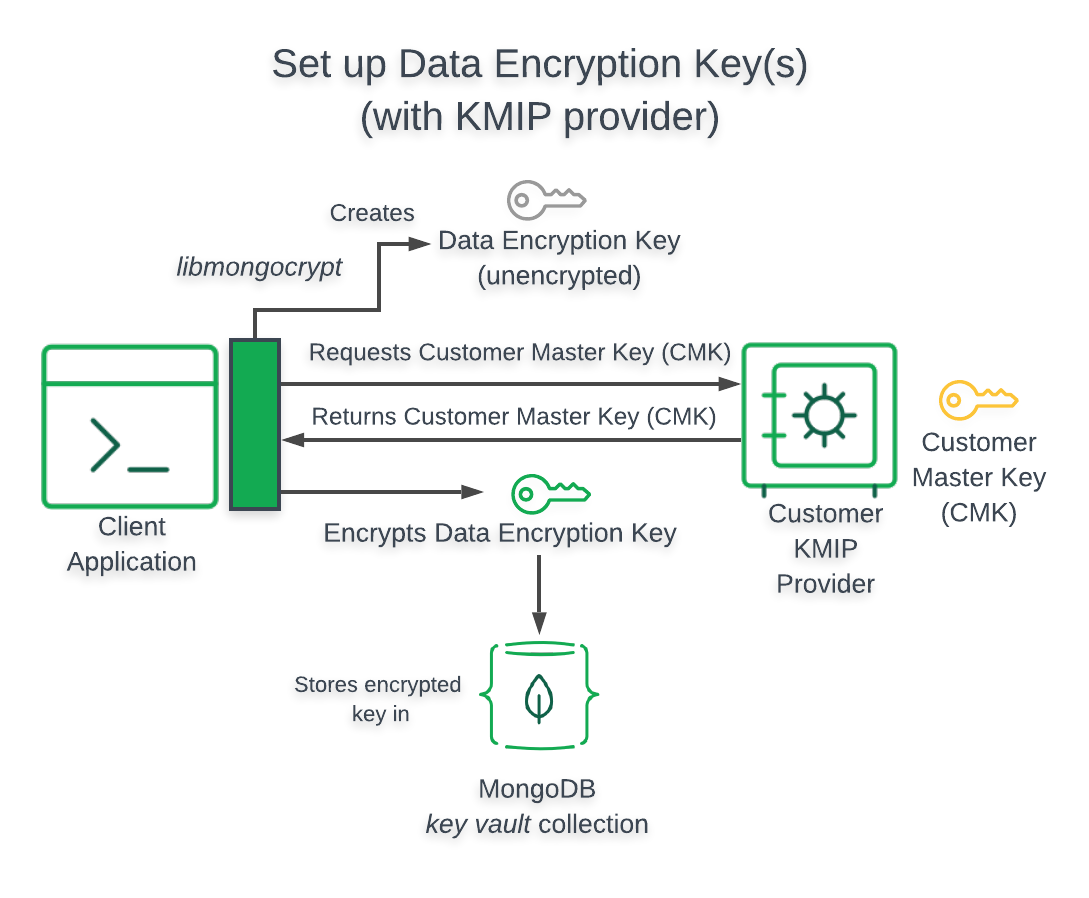
Architecture¶
The following diagram describes the architecture of a -enabled application using a KMIP compliant
provider.
Important
Client Accesses
When your -enabled application uses a KMIP compliant provider, your application directly accesses your .
kmsProviders Object¶
The following table presents the structure of a kmsProviders
object for a KMIP compliant :
Note
Authenticate through TLS/SSL
Your -enabled application authenticates through TLS/SSL when using KMIP.
| Field | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| endpoint | Yes | Specifies a hostname and port number for the authentication server. |
dataKeyOpts Object¶
The following table presents the structure of a dataKeyOpts object
for a KMIP compliant :
| Field | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| keyId | No | The If you do not specify the |
| endpoint | Yes | The URI of your KMIP provider. |
Local Key Provider¶
This section provides information related to using a Local Key Provider (your filesystem) in your -enabled application.
Warning
Do Not Use the Local Key Provider in Production
The Local Key Provider is an insecure method of storage and is not recommended for production. Instead, you should store your s in a remote :wikipedia:` <Key_management#Key_management_system>` (KMS).
To learn how to use a remote KMS in your implementation, see the <csfle-tutorial-automatic-encryption> guide.
To view a tutorial demonstrating how to use a Local Key Provider for testing , see Quick Start.
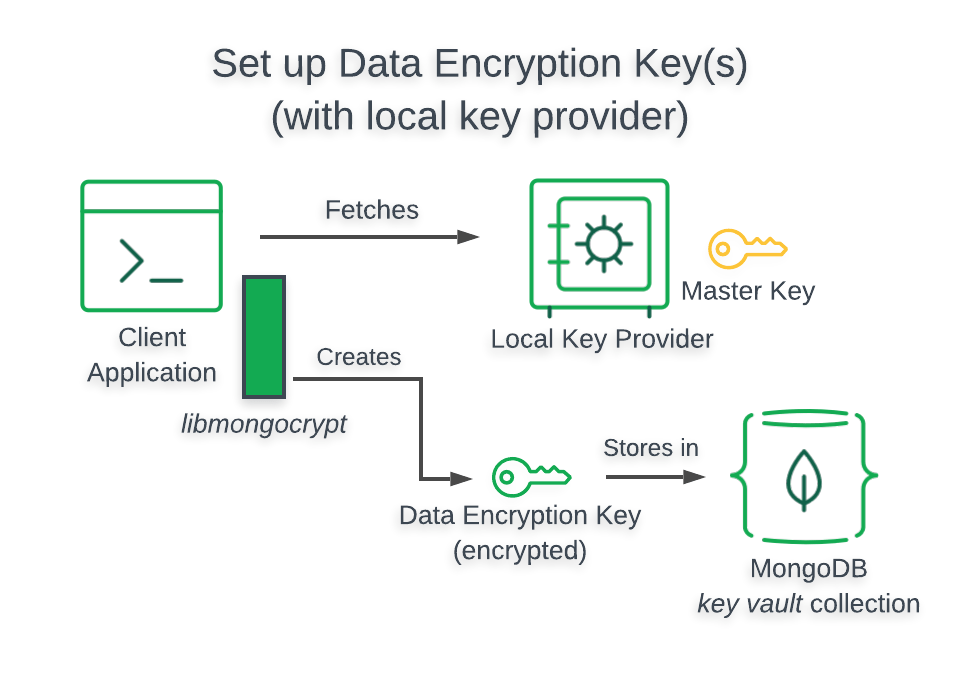
Architecture¶
When you use a Local Key Provider in your -enabled application, your application retrieves your from the filesystem of the computer on which your application is running.
The following diagram describes the architecture of a -enabled application using a Local Key Provider.
kmsProviders Object¶
The following table presents the structure of a kmsProviders
object for a Local Key Provider:
| Field | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| key | Yes | The master key used to encrypt/decrypt data keys. The master key is passed as a base64 encoded string. |
dataKeyOpts Object¶
When you use a Local Key Provider, you specify your
through your kmsProviders object.